A
Vitamins play a crucial role in maintaining good health throughout life. They support essential body functions, fuel metabolic processes, improve immunity, enhance energy levels, and help prevent chronic diseases. While a balanced diet should ideally provide all the vitamins we need, lifestyle changes, stress, food processing, and nutritional gaps often make supplementation helpful or necessary. This guide explores the major vitamins, what they do, where to get them naturally, how much you need, and tips for choosing the right supplement.

Why Vitamins Matter
Every vitamin contributes differently to the body. Some help build strong bones, others boost immunity, improve eyesight, protect cell membranes, or regulate metabolism. Unlike macronutrients such as carbohydrates, fats, and proteins, vitamins are micronutrients—needed in smaller amounts, yet absolutely essential. The body cannot produce most vitamins on its own, so they must come from food or supplements.
A deficiency in even one vitamin can lead to health issues such as fatigue, weakened bones, hair loss, slow metabolism, memory problems, and reduced immune response. On the other hand, too much of certain vitamins can also be harmful, making balance essential.

Water-Soluble vs. Fat-Soluble Vitamins
Vitamins fall into two categories:
1. Water-Soluble Vitamins
These dissolve in water and are not stored in the body. Excess amounts are flushed out through urine. Because they are not stored, daily intake is important.
Water-soluble vitamins include:
- Vitamin C
- B-Complex vitamins: B1, B2, B3, B5, B6, B7, B9 (folate), B12
2. Fat-Soluble Vitamins
These are stored in the liver and fatty tissues and absorbed with dietary fat. Overconsumption can lead to toxicity.
Fat-soluble vitamins include:
- Vitamin A
- Vitamin D
- Vitamin E
- Vitamin K
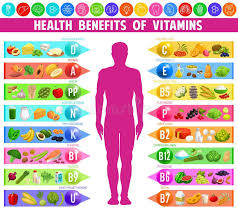
The Essential Vitamins and Their Benefits
1. Vitamin A
Benefits
- Supports vision and eye health
- Enhances immune function
- Helps skin, hair, and nails grow stronger
Best Sources
- Carrots
- Sweet potatoes
- Spinach
- Kale
- Fish and dairy
2. Vitamin B-Complex
Each B vitamin plays a specific role, but together they help convert food into energy, support brain function, and maintain healthy cells.
B Vitamin Highlights
- B1 (Thiamine): metabolism and nerve function
- B2 (Riboflavin): healthy skin, eyes, and energy production
- B3 (Niacin): cholesterol balance and digestion
- B5 (Pantothenic Acid): hormone production
- B6 (Pyridoxine): brain development and neurotransmitters
- B7 (Biotin): healthy hair and nails
- B9 (Folate): essential during pregnancy for fetal development
- B12: red blood cell formation and nerve health
Best Sources
- Whole grains
- Eggs
- Meat and poultry
- Nuts
- Green vegetables

3. Vitamin C
Benefits
- Strengthens the immune system
- Acts as a powerful antioxidant
- Helps absorb iron
- Boosts collagen production for skin and joints
Best Sources
- Citrus fruits
- Bell peppers
- Broccoli
- Strawberries
- Tomatoes

4. Vitamin D
Often called the “sunshine vitamin,” Vitamin D is vital for bone strength and immune defense.
Benefits
- Helps absorb calcium
- Supports mood and emotional health
- Improves immunity
Best Sources
- Sunlight exposure
- Fatty fish
- Egg yolks
- Fortified milk or cereal
5. Vitamin E
Benefits
- Protects cells from oxidative damage
- Supports immunity
- Improves skin health
Best Sources
- Nuts and seeds
- Spinach
- Avocado
- Vegetable oils

6. Vitamin K
Benefits
- Essential for blood clotting
- Supports bone strength
Best Sources
- Leafy greens (kale, spinach, collards)
- Brussels sprouts
- Broccoli
How Much Do You Really Need?
Daily vitamin needs vary by age, gender, and health status. For example:
- Children and adults have different nutritional requirements
- Pregnant women need higher folate and iron
- Older adults may need extra Vitamin B12 and D due to reduced absorption
The best approach is:
- Eat a diverse diet rich in whole foods
- Use a daily multivitamin only if a healthcare professional recommends it
- Avoid megadoses unless medically supervised
Signs of Vitamin Deficiency
Common deficiency symptoms include:
- Fatigue and low energy
- Weak hair and nails
- Frequent infections
- Mood swings or depression
- Poor concentration
- Dry or pale skin
- Muscle cramps or bone pain
If symptoms persist, a blood test can identify specific deficiencies.
Should You Take Supplements?
Supplements can help if:
- Your diet lacks variety
- You have medical conditions that affect absorption
- You follow a restrictive diet (vegan, low-calorie, low-fat)
- You are over age 50
- You are pregnant or planning a pregnancy
However:
- Supplements are not a replacement for healthy eating
- Not all supplements are created equal
- High doses of fat-soluble vitamins can be harmful
When choosing supplements:
- Look for third-party tested brands
- Prefer those with clearly listed doses and forms
- Avoid unnecessary fillers, artificial colors, and megadoses
How to Improve Vitamin Absorption
1. Pair Vitamins With the Right Foods
- Fat-soluble vitamins absorb better with healthy fats (olive oil, nuts, fish)
- Vitamin C enhances iron absorption
2. Avoid Overcooking
High heat destroys Vitamin C and many B vitamins. Try:
- Steaming
- Stir-frying
- Light roasting
3. Spread Intake Throughout the Day
Water-soluble vitamins work better when taken in smaller doses over time.
Building a Vitamin-Rich Daily Diet
Sample one-day plan:
- Breakfast: oatmeal with fresh berries and nuts
- Lunch: spinach salad with eggs, avocado, and olive oil dressing
- Snack: orange or carrot sticks
- Dinner: grilled salmon with sweet potatoes and broccoli
This gives a natural variety of vitamins A, B, C, D, E, and K.
Final Thoughts
Vitamins are essential building blocks of lifelong health. They:
- Strengthen immunity
- Feed the brain
- Energize the body
- Protect against diseases
- Support strong bones and youthful skin
While a balanced diet remains the best source of vitamins, supplements can play a valuable role when used responsibly. Understanding what each vitamin does, where to get it, and how much you need empowers you to make smarter choices for your health today and in the future.

If you’d like, I can also provide:
✔ a shorter 300-word version
✔ a kid-friendly version
✔ a vitamin chart/infographic
✔ food plan for a week
✔ sources and references
Just tell me what you want!
